Solved Problem on Static Equilibrium
advertisement
Two identical spheres, A and B, are placed in a box. The line connecting the centers of
the two spheres makes an angle of 45° with the horizontal, and the reaction force exerted by the bottom
of the box on sphere B is 25 N. Determine the reaction force that the box exerts on the spheres at
the points of contact between the spheres and the box, and the force that sphere A exerts on
sphere B.

Problem data:
- Reaction force of the bottom of the box on sphere B: FR = 25 N;
- Angle between the line connecting the centers of the spheres and the horizontal: θ = 45°;
- Acceleration due to gravity: g = 9.8 m/s2.
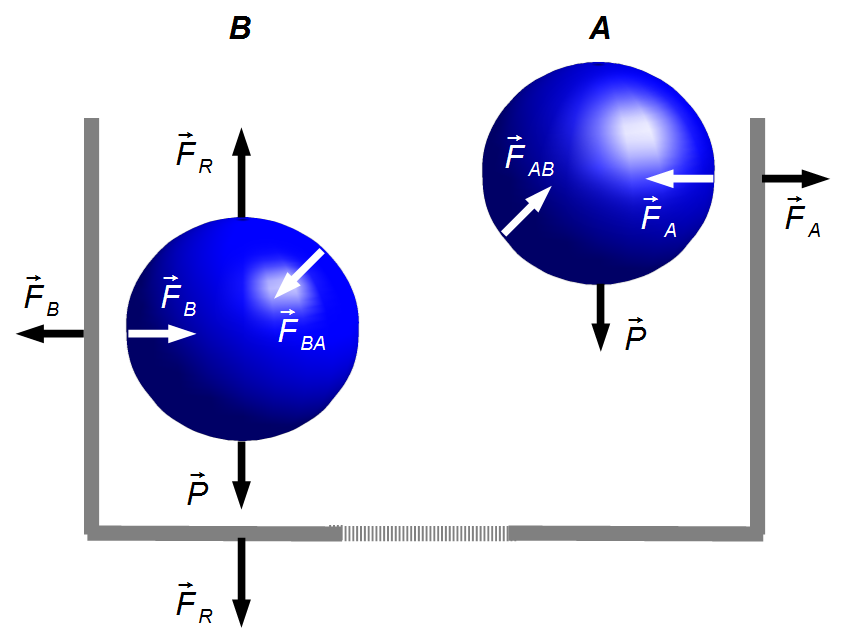
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams, we have the forces acting on the blocks (Figure 1).
-
Box:
- \( -{\vec F}_R \): force that sphere B exerts on the bottom of the box;
- \( {\vec F}_A \): force that sphere A exerts on the side wall of the box;
- \( -{\vec F}_B \): force that sphere B exerts on the side wall of the box.
-
Sphere A:
- \( {\vec F}_g \): gravitational force of sphere A;
- \( {\vec F}_{AB} \): contact force on sphere A due to sphere B;
- \( -{\vec F}_A \): reaction force of the box on sphere A.
-
Sphere B:
- \( {\vec F}_g \): gravitational force of sphere B;
- \( {\vec F}_{BA} \): contact force on sphere B due to sphere A, \( |\;{\vec{F}}_{BA}\;|=|\;{\vec{F}}_{AB}\;| \);
- \( {\vec F}_R \): reaction force of the bottom of the box on sphere B;
- \( {\vec F}_{B} \): reaction force of the box on sphere B.
Since the system is in equilibrium, the resultant of the forces is equal to zero.
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#99CCFF,10px]
{\sum _i F_i=0} \tag{I}
\end{gather}
\]
We draw the forces in an xy coordinate system (Figures 2 and 3) and obtain their components along the
x and y directions.
- Sphere A:
- x-direction:
- \( F_{Ax}=-F_A \)
- \( F_{ABx}=F_{AB}\cos\theta \)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{ABx}-F_A=0 \\[5pt]
F_{AB}\cos\theta-F_A=0 \tag{II}
\end{gather}
\]

- Sphere A:
- y-direction:
- \( F_{gy}=-F_g \)
- \( F_{ABy}=F_{AB}\sin\theta \)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{ABy}-F_{gy}=0 \\[5pt]
F_{AB}\sin \theta-F_g=0 \tag{III}
\end{gather}
\]
The gravitational force is given by
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#99CCFF,10px]
{P=mg} \tag{IV}
\end{gather}
\]
substituting equation (IV) into equation (III)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{AB}\sin\theta-mg=0 \tag{V}
\end{gather}
\]
- Sphere B:
- x-direction:
- \( F_{Bx}=F_B \)
- \( F_{BAx}=-F_{BA}\cos\theta=-F_{AB}\cos\theta \)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_B-F_{BAx}=0 \\[5pt]
F_B-F_{AB}\cos\theta=0 \tag{VI}
\end{gather}
\]
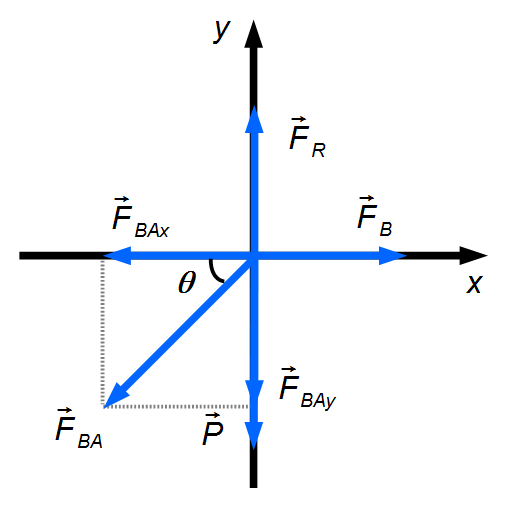
- Sphere B:
- y-direction:
- \( F_{gy}=-F_g \)
- \( F_{Ry}=F_R \)
- \( F_{BAy}=-F_{BA}\sin\theta-F_{AB}\sin\theta \)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_R-F_{BAy}-P=0 \\[5pt]
F_R-F_{AB}\sin\theta-P=0 \tag{VII}
\end{gather}
\]
substituting equation (IV) into equation (VII)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_R-F_{AB}\sin\theta-mg=0 \tag{VIII}
\end{gather}
\]
Equations (II), (III), and (VIII) can be written as a system of three equations with four unknowns
(FA, FAB, m and θ)
\[
\begin{gather}
\left\{
\begin{array}{l}
F_B-F_{AB}\cos\theta=0 \\
F_{AB}\cos\theta-F_A=0 \\
F_{AB}\sin\theta-mg=0 \\
F_R-F_{AB}\sin\theta-mg=0
\end{array}
\right.
\end{gather}
\]
from the third equation of the system, we write
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{AB}\sin\theta-mg=0 \\[5pt]
F_{AB}\sin\theta=mg
\end{gather}
\]
substituting this value into the fourth equation of the system
\[
\begin{gather}
F_R-mg-mg=0 \\[5pt]
2mg=F_R \\[5pt]
m=\frac{F_R}{2g} \\[5pt]
m=\frac{25\;\mathrm N}{2\times 9.8\;\mathrm{\frac{m}{s^2}}}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{m=1.28\;\mathrm{kg}}
\end{gather}
\]
Substituting this value of mass into the third equation of the system
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{AB}\operatorname{sen}\theta-mg=0 \\[5pt]
F_{AB}=\frac{mg}{\operatorname{sen}\theta}
\end{gather}
\]
From Trigonometry, for θ = 45°,
\( \cos 45°=\operatorname{sen}45°=\frac{\sqrt{2\;}}{2} \)
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{AB}=\frac{(1.28\;\mathrm{kg})\left(9.8\;\mathrm{\frac{m}{s^2}}\right)}{\dfrac{\sqrt{2\;}}{2}}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{F_{AB}=17.7\;\mathrm N}
\end{gather}
\]
Substituting this value of the force between spheres A and B into the first and second
equations of the system
\[
\begin{gather}
F_B-F_{AB}\cos\theta=0 \\[5pt]
F_B=F_{AB}\cos\theta \\[5pt]
F_B=(17.7\;\mathrm N)\times\frac{\sqrt{2\;}}{2}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{F_B=12.5\;\mathrm N}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
F_{AB}\cos\theta-F_A=0 \\[5pt]
F_A=F_{AB}\cos\theta \\[5pt]
F_A=(17.7\;\mathrm N)\times\frac{\sqrt{2\;}}{2}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{F_A=12.5\;\mathrm N}
\end{gather}
\]
advertisement

Fisicaexe - Physics Solved Problems by Elcio Brandani Mondadori is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .